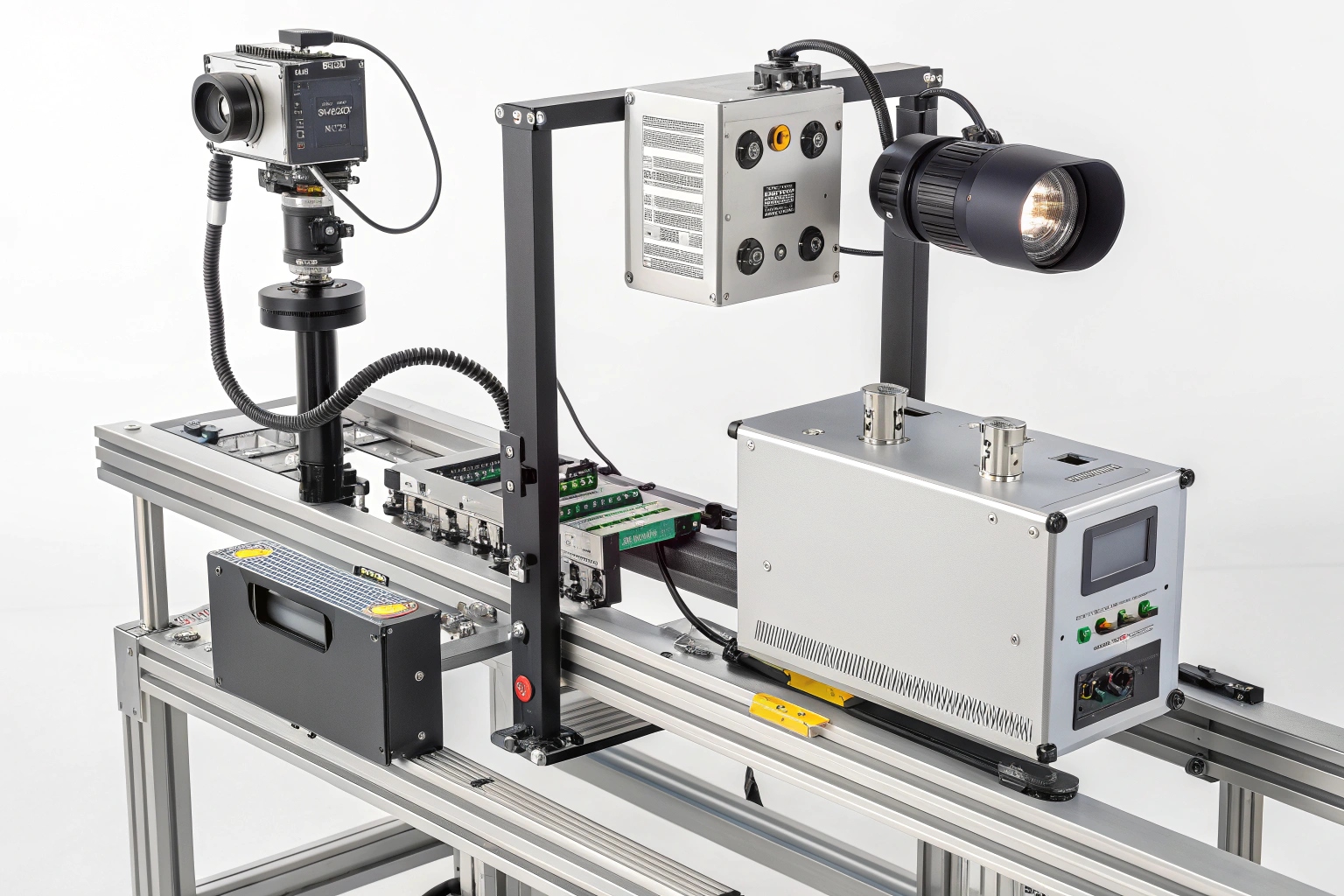

Manufacturing quality control seems impossible without proper inspection systems. Many companies struggle with inconsistent product quality and costly defects.
A visual inspection system is an automated quality control technology that uses cameras, lighting, and software algorithms to detect defects, measure dimensions, and verify product specifications without human intervention. These systems combine hardware components like industrial cameras and specialized lighting with advanced image processing software.

As a supplier in the manufacturing industry, I have seen how visual inspection systems transform production lines. These systems catch defects that human eyes might miss and work 24/7 without fatigue.
What are the 4 types of inspection?
Quality control requires different inspection approaches depending on your production needs. Each method serves specific manufacturing requirements and cost considerations.
The four main types of inspection in manufacturing are: 100% inspection (examining every product), sampling inspection (checking selected items), first article inspection (validating initial production), and patrol inspection (periodic quality checks throughout production).
Each inspection type serves different purposes in quality control. 100% inspection works best for critical components where every defect matters. I remember working with a pencil manufacturer in Japan who used 100% inspection for premium pencil leads. The cost was high but zero defects reached customers.
Sampling inspection reduces costs while maintaining quality standards. Statistical methods determine sample sizes based on acceptable quality levels. This approach works well for high-volume production where testing every item is impractical.
First article inspection validates that production setup meets specifications before full production begins. This prevents entire batches from being defective. Production teams check dimensions, materials, and processes against engineering drawings and specifications.
| Inspection Type | When to Use | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% Inspection | Critical components | Zero defects escape | High cost and time |
| Sampling | High volume production | Cost effective | Some defects may pass |
| First Article | New production runs | Prevents batch defects | Only checks setup |
| Patrol | Ongoing production | Monitors process stability | May miss some issues |
Patrol inspection1 involves regular quality checks2 during production. Inspectors move through production areas checking processes and products at scheduled intervals. This method catches problems early before they affect large quantities.
What is the ISO standard for visual inspection?
International standards ensure consistent quality practices across different industries and countries. Understanding these standards helps manufacturers meet global requirements.
No single ISO standard specifically covers "visual inspection" alone. Instead, several ISO standards address visual inspection as part of broader quality management systems, including ISO 2859 series for sampling procedures, ISO 9001 for quality management, and industry-specific standards like IATF 16949 for automotive.

The ISO 2859 series provides sampling procedures for inspection by attributes. These standards help manufacturers determine appropriate sample sizes and acceptance criteria. Part 1 covers indexing schemes for lot-by-lot inspection. Part 2 addresses sampling plans for isolated lots.
ISO 9001 establishes quality management system requirements. Section 8.5 covers production and service provision. This includes monitoring and measuring processes to ensure products meet requirements. Visual inspection often serves as a key monitoring method.
Industry-specific standards build upon general ISO requirements. IATF 169493 adds automotive-specific requirements to ISO 9001. ISO 134854 covers medical device quality management. These standards often mandate specific inspection and testing methods.
| Standard | Scope | Visual Inspection Role |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 2859-1 | Sampling procedures | Defines acceptance sampling plans |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management | Requires process monitoring |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive quality | Mandates specific inspection methods |
| ISO 13485 | Medical devices | Requires validation of inspection systems |
| ISO 14155 | Clinical investigation | Covers inspection of medical device trials |
Other relevant standards include ISO/IEC Guide 98 for measurement uncertainty and ISO 10012 for measurement management systems. These provide guidance on ensuring measurement reliability and traceability.
What are the main points of visual inspection?
Effective visual inspection requires careful attention to several critical factors. These elements determine whether your inspection system delivers reliable and consistent results.
The main points of visual inspection include: establishing clear inspection criteria, maintaining consistent imaging conditions, selecting appropriate hardware components, implementing robust and validated algorithms, training qualified personnel, and ensuring proper documentation and traceability.

Clear inspection standards form the foundation of effective visual inspection. Standards must specify exactly what constitutes acceptable and unacceptable products. Written procedures eliminate subjective interpretations. Visual aids like reference samples help inspectors understand requirements.
Consistent imaging environment ensures reliable detection. Lighting type, intensity, and angle affect what cameras see. Temperature, vibration, and electromagnetic interference can impact results. Environmental controls maintain stable conditions throughout production shifts.
Hardware selection matches inspection requirements. Camera resolution determines the smallest detectable defects. Lens selection affects field of view and working distance. Lighting technology influences contrast and visibility. Processing power determines inspection speed and complexity.
| Factor | Requirements | Impact on Results |
|---|---|---|
| Lighting | Consistent intensity and angle | Affects defect visibility |
| Camera resolution | Matches smallest defect size | Determines detection capability |
| Lens selection | Appropriate magnification | Controls field of view |
| Processing power | Handles algorithm complexity | Affects inspection speed |
| Environmental control | Stable temperature and vibration | Ensures consistent performance |
Algorithm validation5 ensures accurate detection. Test data must cover all expected defect types and normal variations. False positive and false negative rates need optimization. Regular validation maintains performance over time as conditions change.
Documentation and traceability support quality systems. Inspection results link to specific products and production times. Statistical analysis6 identifies trends and improvement opportunities. Calibration records7 demonstrate measurement accuracy.
How is AI used in visual inspection?
Artificial intelligence transforms traditional visual inspection from rule-based systems to learning-based approaches. This shift enables detection of complex defects that challenge conventional methods.
AI in visual inspection uses deep learning algorithms to automatically learn defect patterns from training data, enabling detection of complex irregularities, improved classification accuracy, anomaly detection, enhanced adaptability to varying conditions, and reduced false alarm rates compared to traditional rule-based systems.

Traditional visual inspection relies on predefined rules and algorithms. Engineers must program specific criteria for each defect type. This approach struggles with irregular patterns, texture variations, and complex surface conditions. Environmental changes require manual adjustments to maintain accuracy.
Deep learning revolutionizes defect detection by learning patterns automatically. Convolutional neural networks analyze thousands of images to identify defective features. The system learns what normal products look like and flags anomalies without explicit programming.
Complex defect handling represents AI’s biggest advantage. Scratches, dents, and surface irregularities vary greatly in appearance. Traditional systems struggle to define rules covering all variations. AI learns these patterns naturally through training examples.
Classification and recognition capabilities exceed human performance in many applications. AI systems differentiate between defect types automatically. This enables sorting products by defect severity rather than simple pass/fail decisions. Multiple defect detection occurs simultaneously in single inspections.
| Traditional Inspection | AI-Powered Inspection |
|---|---|
| Rule-based algorithms | Learning-based patterns |
| Struggles with complex defects | Handles irregular patterns |
| Sensitive to environmental changes | Adapts to varying conditions |
| High false alarm rates | Reduced false positives |
| Manual programming required | Automatic feature learning |
| Limited defect classification | Multiple defect recognition |
Anomaly detection8 identifies previously unknown defect types9. Traditional systems only detect programmed defects. AI recognizes when products differ significantly from normal patterns, even for defects not seen during training.
Adaptability and robustness improve system reliability10. AI systems adjust to lighting changes, product variations, and environmental factors. Continuous learning updates models as new data becomes available. This reduces maintenance requirements and improves long-term performance.
The shift from manual rule creation to machine learning11 represents a fundamental change in quality control philosophy. AI enables visual inspection systems12 to become more intelligent, flexible, and effective in complex manufacturing environments.
Conclusion
Visual inspection systems combine cameras, lighting, and software to automate quality control, with AI transforming traditional rule-based approaches into intelligent learning systems.
-
Understanding Patrol inspection can enhance your quality control processes and help catch issues early. ↩
-
Exploring the role of quality checks can provide insights into boosting production efficiency and reducing waste. ↩
-
Exploring this link will provide you with detailed insights into the automotive-specific requirements that enhance quality management. ↩
-
This resource will help you understand the critical role of ISO 13485 in ensuring quality management for medical devices. ↩
-
Understanding algorithm validation is crucial for ensuring accurate detection and optimizing performance in various applications. ↩
-
Understanding statistical analysis can enhance your knowledge of quality systems and help identify trends for improvement. ↩
-
Exploring calibration records will provide insights into maintaining accuracy and reliability in quality control processes. ↩
-
Understanding anomaly detection can enhance your knowledge of AI’s capabilities in identifying defects. ↩
-
Exploring various defect types can help you grasp the complexities of quality control in production. ↩
-
Exploring this resource will provide insights into enhancing system reliability, crucial for maintaining performance and reducing downtime. ↩
-
Explore how machine learning enhances quality control processes, making them more efficient and accurate. ↩
-
Learn about the advancements in visual inspection systems and their impact on manufacturing quality and efficiency. ↩
Written by
You may also be interested in:

What is the Standard for Visual Inspection?
Are you struggling with incons

What is a visual inspection machine?
You face quality control chall
