
You face quality control challenges every day. Manual inspection is slow and inconsistent. Visual inspection machines automate this critical process.
A visual inspection machine is automated equipment that uses optical imaging and computer technology to simulate human visual functions. It captures product images through cameras and analyzes them via computer systems to identify, detect, and classify items automatically.

I have worked with countless manufacturers who struggled with quality control. They needed consistent, reliable inspection systems. Visual inspection machines became their solution.
What is included in a visual inspection?
Your inspection process needs comprehensive coverage. Missing defects costs money and damages reputation. What elements should you include?
Visual inspection includes defect detection, product sorting and classification, item counting and dimensional measurement, plus target identification and tracking. These four core functions ensure complete quality assessment.

Based on my experience serving clients across different industries, visual inspection encompasses four main functions. First is defect detection1. The system identifies surface scratches, cracks, discoloration, or shape irregularities. I have seen this applied in automotive manufacturing2 where it catches minute scratches on metal parts that human eyes might miss.
Second comes product sorting and classification3. The machine categorizes items based on size, color, shape, or quality grades. In seed agriculture, clients use this to separate premium seeds4 from lower quality ones. The precision amazes me every time.
| Function | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Defect Detection | Surface scratches, cracks | 99.9% accuracy |
| Product Sorting | Size, color classification | Automated grading |
| Item Counting | Quantity verification | Inventory control |
| Target Tracking | Object positioning | Real-time monitoring |
Third is product counting5 and dimensional measurement6. The system counts items accurately and measures dimensions to ensure specifications. Packaging companies rely on this for consistent fill weights and counts.
Fourth involves target identification and tracking7. The system recognizes specific objects and tracks their movement. This technology powers autonomous vehicles8 and security systems I have installed for clients.
How many types of visual inspection are there?
You need to choose the right inspection technology. Different applications require different approaches. Which type fits your needs?
There are primarily two types of visual inspection systems: 2D visual inspection and 3D visual inspection. 2D systems analyze flat surface features while 3D systems provide depth and volume measurements for complex geometries.
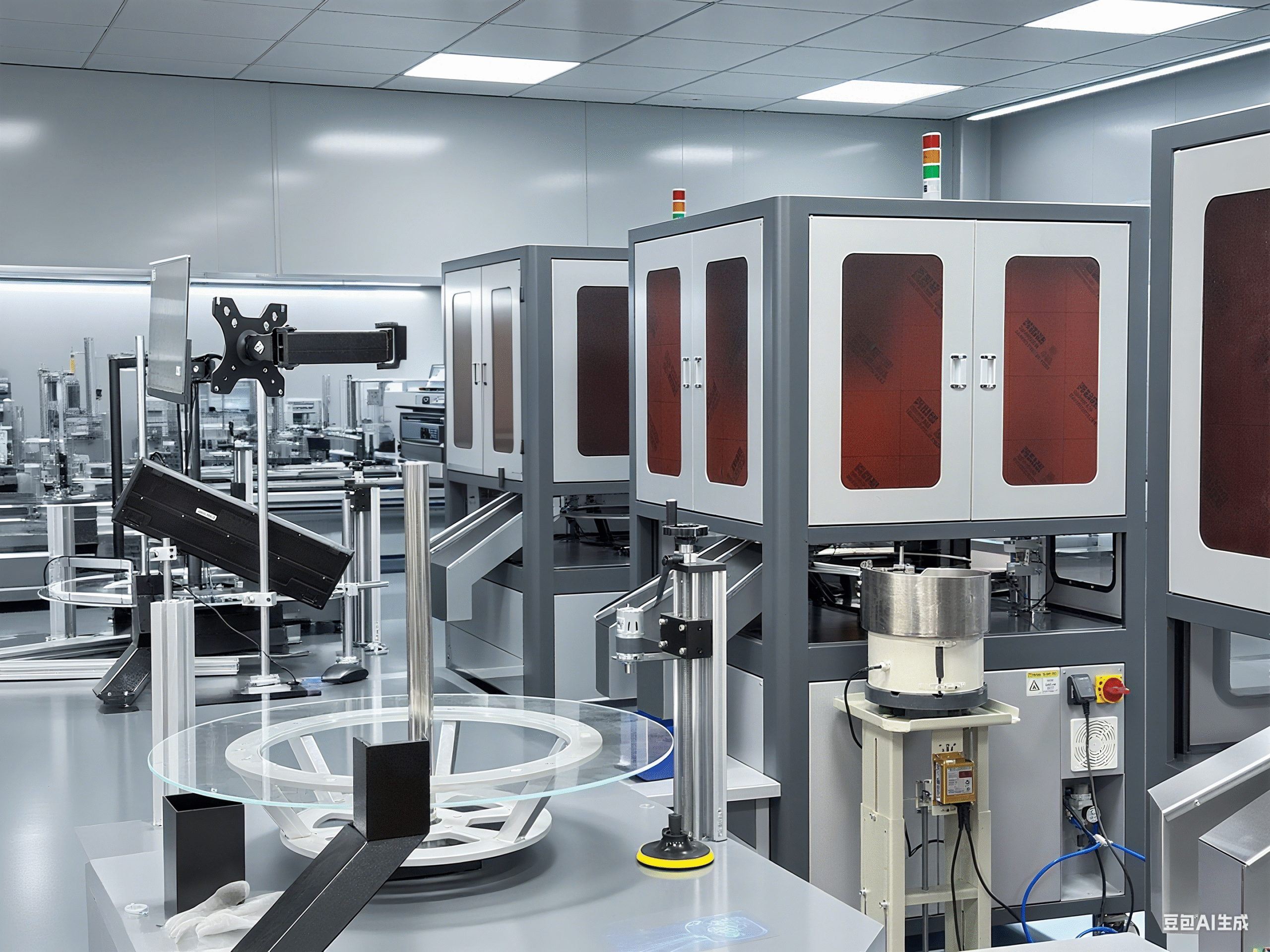
From my technical experience, visual inspection systems divide into two main categories based on dimensional analysis capabilities.
2D visual inspection systems analyze flat surface characteristics. They excel at detecting surface defects, measuring length and width, reading text or codes, and color verification. I recommend these systems for electronics manufacturing where circuit board inspection requires high precision but depth measurement is not critical. The processing speed is faster and costs are lower.
3D visual inspection systems capture height, depth, and volume information. They create detailed three-dimensional models of objects. These systems work perfectly for automotive parts where bolt head height or connector insertion depth matters. I have installed these systems in food processing facilities where volume measurement ensures consistent portion sizes.
The choice depends on your specific requirements. Surface-only inspection needs 2D systems. Complex geometry verification requires 3D capability. Many clients start with 2D systems and upgrade to 3D as their quality requirements increase.
What are the main points of visual inspection?
Your inspection results must be consistent and reliable. Poor setup leads to false positives and missed defects. What factors determine success?
The main points of visual inspection focus on three critical parameters: industrial camera selection, lens compatibility, and lighting optimization. These elements work together to ensure stable and accurate inspection results.

Based on feedback from our technical expert Master Wang, three parameters determine inspection accuracy and stability.
Industrial camera selection comes first. CCD sensor cameras provide superior image quality and stability compared to CMOS alternatives. The sensor size and resolution must match your inspection requirements. Higher resolution captures more detail but processes slower. I balance these factors based on each client’s production speed needs.
Lens compatibility follows close behind. The lens resolution must exceed the camera’s limit resolution capabilities. This ensures the camera sensor receives maximum detail. Working distance, field of view, and magnification ratios need careful calculation. I have seen perfect cameras fail because of poor lens matching.
| Component | Key Specification | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Camera | CCD sensor preferred | Image stability |
| Lens | Resolution > camera limit | Detail capture |
| Lighting | LED visible light | Consistent illumination |
Lighting optimization completes the trinity. LED light sources provide consistent, stable illumination compared to traditional options. The lighting angle, intensity, and color temperature affect contrast and detail visibility. Even shadows can hide critical defects.
Environmental stability cannot be ignored either. Temperature fluctuations affect camera sensitivity. Vibrations blur images. Electrical noise corrupts signals. I always recommend installing systems on solid, vibration-free foundations with stable power supplies.
What are the equipment used in visual inspection?
You need reliable components for consistent results. Equipment selection affects your entire system performance. Which components matter most?
Visual inspection equipment consists of three main components: industrial lenses for image capture, vision inspection light sources for illumination, and controllers for processing and decision making. These components work as an integrated system.
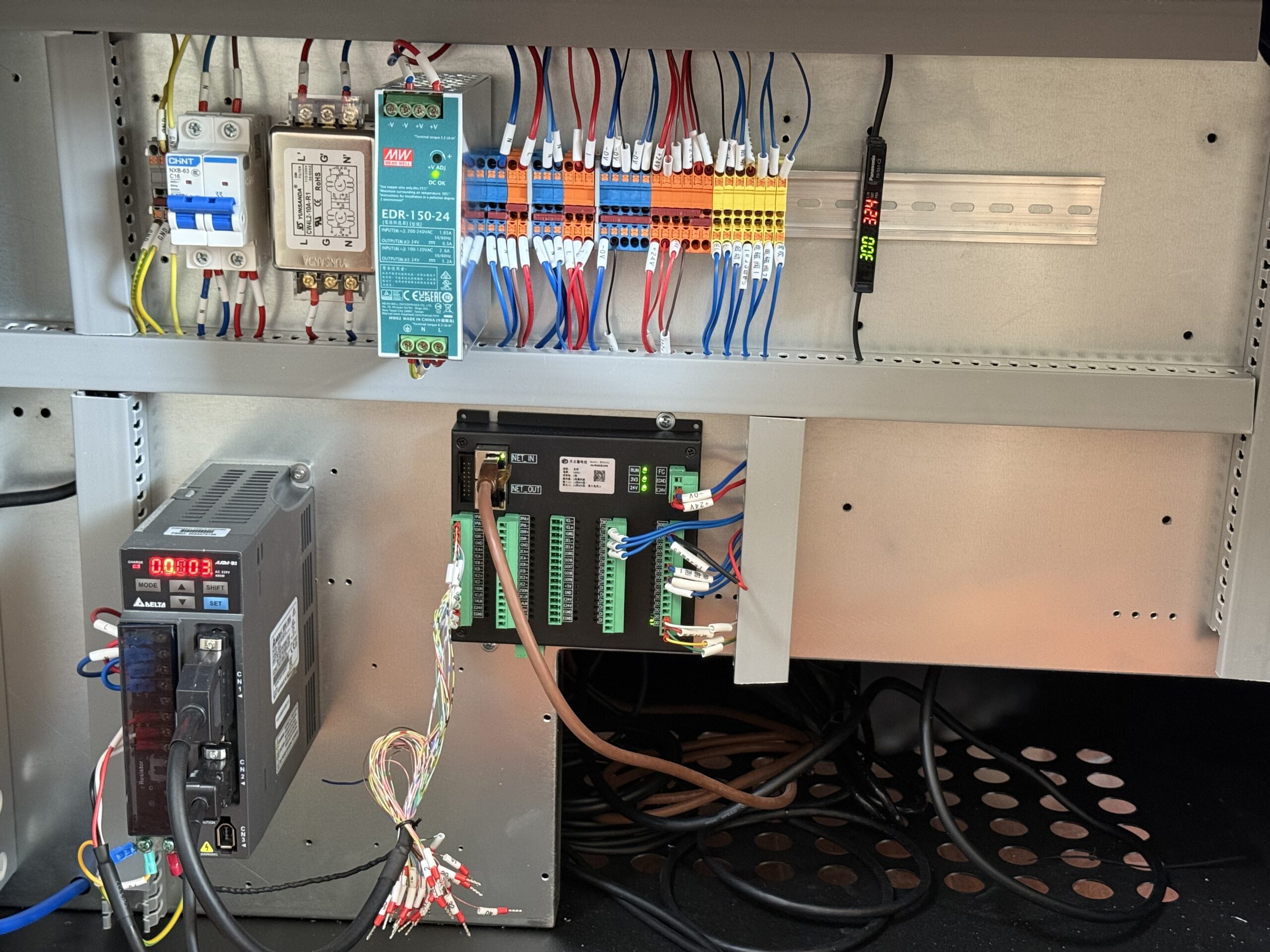
My experience installing hundreds of systems taught me that three core components determine system success.
Industrial lenses serve as the system eyes. They capture product images with precise focus and minimal distortion. Lens selection depends on working distance, field of view requirements, and magnification needs. Fixed focal length lenses offer better optical performance than variable zoom options. I prefer telecentric lenses for dimensional measurement applications because they eliminate perspective errors.
Vision inspection light sources provide controlled illumination. LED arrays offer consistent brightness, long lifespan, and instant on-off capability. Ring lights work well for general inspection. Backlights reveal edge details and transparency issues. Dome lights eliminate shadows on curved surfaces. Side lighting enhances surface texture visibility.
Controllers process captured images and make inspection decisions. They run analysis algorithms, compare results against specifications, and trigger sorting mechanisms. Processing power determines inspection speed. Memory capacity affects algorithm complexity. I recommend controllers with expansion capability for future upgrades.
Additional components include positioning systems for repeatable part placement, sorting mechanisms for automated handling, and communication interfaces for production line integration. Each component must work reliably under industrial conditions with minimal maintenance requirements.
Conclusion
Visual inspection machines automate quality control through integrated camera, lighting, and processing systems. Proper component selection and environmental control ensure consistent, reliable results for manufacturing applications.
-
Understanding defect detection is crucial for improving quality control in manufacturing processes. ↩
-
Exploring this link will reveal how visual inspection enhances quality and efficiency in the automotive industry. ↩
-
Explore how product sorting enhances efficiency and quality in agriculture, ensuring better yields and customer satisfaction. ↩
-
Learn about the advantages of using premium seeds for better crop performance and higher returns on investment. ↩
-
Explore this link to learn effective strategies for accurate product counting, essential for maintaining quality in packaging. ↩
-
Discover how dimensional measurement ensures product quality and compliance in packaging, crucial for business success. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand cutting-edge developments in target identification and tracking, crucial for various applications. ↩
-
Discover how autonomous vehicles leverage this technology for safety and efficiency, enhancing your knowledge of modern transport. ↩
Written by
You may also be interested in:

What is a visual inspection system?
Manufacturing quality control

What is the Standard for Visual Inspection?
Are you struggling with incons
